

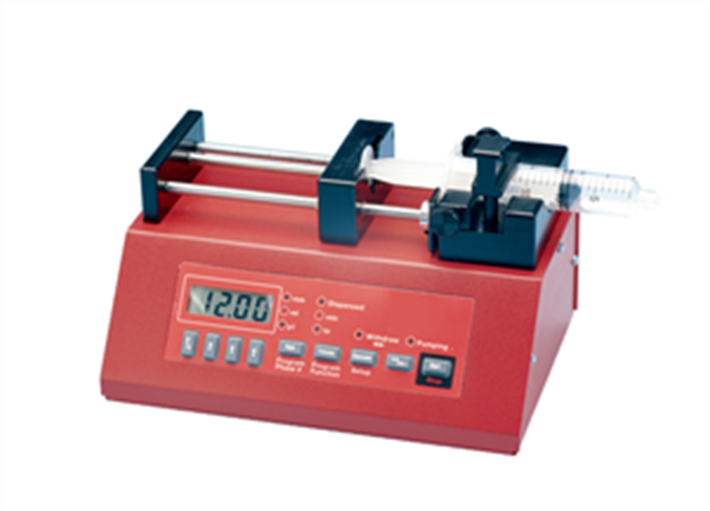
SYS-PV830
Pneumatic PicoPump with vacuum
- Overview
- Specifications
- Accessories
- Citations
- Related Products
Overview


There are 2 images available to view - click to enlarge and scroll through the product gallery.
Instruction Manual
/ Download as PDF
PV830 Pneumatic PicoPump Injector Sales Sheet
/ Download as PDF
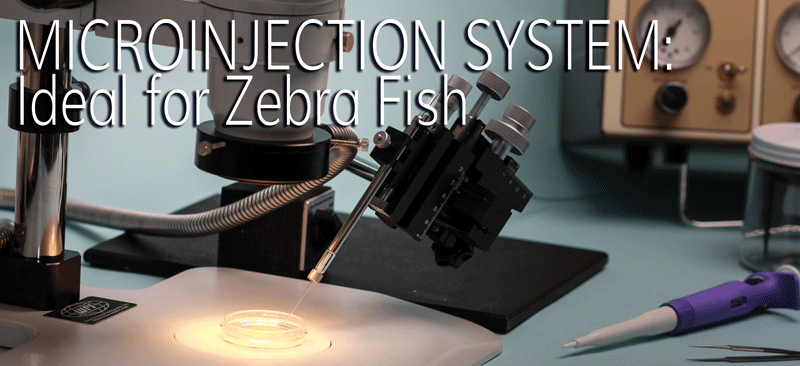
Zebrafish Microinjection Setup
/ Download as PDF
Microinjection Datasheet
/ Download as PDF
- Regulated Hold, Ejection and Vacuum Pressure
- Carefully regulated air pressures for securing cells and injecting them with fluid
- Pressure Input: 0-150 psi
- Pressure Output: 0.3-90 psi
Intracellular injection
Designed to simplify intracellular injection and a variety of other microinjection tasks, WPI™s PicoPumps use carefully regulated air pressures for securing cells and injecting them with fluid. Injected volumes range from picoliters to nanoliters. Separate ports supply positive and negative pressure - positive pressure for high-pressure ejection, and suction for supporting the cell or for filling the pipette from the tip. A second pressure port maintains a low positive "holding" pressure to the injecting pipette between injection pulses, to prevent fluid uptake through capillary action or diffusion. Timing, ejection pressure, holding pressure, and suction are adjusted independently by control knobs and indicator gauges on the front panel. Injection pressure is controlled by a 20-turn regulator on the front panel. A built-in timing circuit allows precise control of the amount of time that the injection pressure is applied to the output port. Time intervals can range from 10 seconds down to 10 ms or less, depending on the eject pressure setting. The injection pressure interval can be triggered manually on the front panel, by footswitch, or by computer controlled TTL pulse. A 5 volt monitor output provides a logic-level pulse for your computer or other monitoring device.
PV830 Features
Eject pressure, Hold pressure, and Vacuum are all available, controlled by separate regulators on the front panel. Eject pressure supplies a high-pressure pulse for injecting fluid. Hold pressure, which is not sufficient to cause fluid ejection, is used to prevent back filling of the pipette by capillary action or diffusion when the solenoid is inactive. Pressure in the injection pipette is automatically switched between Eject and Hold pressure by a precision timing circuit that controls a solenoid valve. Vacuum is used to fill pipettes from the tip or to secure a floating cell during microinjection. Vacuum is regulated the same way, by a 20-turn knob on the front panel. Vacuum may be switched from regulated vacuum to atmosphere by using the pneumatic toggle on the front panel. Vacuum can also be routed to the eject port.
Ideal for zebrafish microinjection systems.
Specifications
PRESSURE
| Pressure Input | 0-150PSI |
| Pressure Output | 0.3-90PSI |
| Lowest Regulated Pressure | 12" water |
| Regulator Accuracy | 0.1% (20-turn dial) |
| Regulator Repeatability | 0.05PSI (both hold and eject pressures) |
| Gauge Accuracy | 3% at full scale (both hold and eject pressures) |
| Input Connector | Quick Connect (1/4" OD tubing) |
| Output Connector | Barbed (1/16" ID tubing) |
| Control | Solenid |
VACUUM
| Vacuum Input | 0-30.0" Hg |
| Vacuum Output | 0.2-29.9" Hg |
| Lowest Regulated Vacuum | 3" water |
| Regulator Accuracy | 0.1% (20-turn dial) |
| Regulator Repeatability | 0.03" Hg |
| Gauge Accuracy | 3% at full scale |
| Input Connector | Quick Connect (1/4" OD tubing) |
| Output Connector | Barbed (1/16" ID tubing) |
| Control | Manual |
| Vent | Atmosphere |
CONNECTIONS INCLUDED
| Input Kit | 10' nylon tubing (0.25" OD, 1000PSI), one 1/2" female NPT adapter |
| Output Kit | Two PicoNozzle |
PHYSICAL SPECS
| Power | 95-135V or 220-240V, 50/60Hz |
| Dimensions | 17 x5.25 x 9.5" (43 x 13 x 24cm) |
| Shipping Weight | 14 lb. (6.3kg) |
Accessories
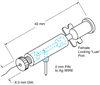
MPH6R
Microelectrode Holder, Male Connector, Wire Half-Cell, Female Luer, Screw Cap. For use ...
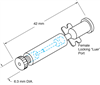
5430-12
PicoNozzle Kit (for 1.2mm pipette) For use with the PicoPumps For use with 1.2mm pip...
5430-15
PicoNozzle Kit (for 1.5 mm pipette) For use with the PicoPumps For use with 1.5 mm p...
5430-20
PicoNozzle Kit (for 2.0mm pipette) For use with the PicoPumps For use with 2.0 mm pi...
MPH6S
Microelectrode Holder, Female Luer, Screw Cap. For use with these WPI Products: Piconoz...
Citations
Ewart, M., Kennedy, S., MacMillan, D., & Raja, A. (2014). Altered vascular smooth muscle function in the ApoE knockout mouse during the progression of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021915014001129
Hall, J., Jheon, A., Ealba, E., & Eames, B. (2014). Evolution of a developmental mechanism: Species-specific regulation of the cell cycle and the timing of events during craniofacial osteogenesis. Developmental …. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012160613006118
Huang, B., & Gale, D. (2014). Stent with preferential coating. US Patent 8,709,071. Retrieved from https://www.google.com/patents/US8709071
Kongton, K., McCall, K., & Phongdara, A. (2014). Identification of gamma-interferon-inducible lysosomal thiol reductase (GILT) homologues in the fruit fly< i> Drosophila melanogaster. Developmental & Comparative …. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0145305X14000081
Nagase, M., & Takahashi, Y. (2014). On-Site Energy Supply at Synapses through Monocarboxylate Transporters Maintains Excitatory Synaptic Transmission. The Journal of …. Retrieved from https://www.jneurosci.org/content/34/7/2605.short
Saralahti, A., & Piippo, H. (2014). Adult zebrafish model for pneumococcal pathogenesis. Developmental & …. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0145305X13002619
Shi, Y., Yao, J., Xu, G., & Taber, L. (2014a). Accepted Manuscript Not Copyedited. Retrieved from https://biomechanical.asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/data/Journals/JBENDY/0/BIO-13-1491.pdf
Shi, Y., Yao, J., Xu, G., & Taber, L. (2014b). Bending of the Looping Heart: Differential Growth Revisited. Journal of …. Retrieved from https://gasturbinespower.asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/article.aspx?articleid=1829834
Tajima, Y., Takuwa, H., & Nishino, A. (2014). Cerebral hemodynamic response to acute hyperoxia in awake mice. Brain research. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006899314001413
Tang, P., & Watson, G. (2014). Cadherin-23 May Be Dynamic in Hair Bundles of the Model Sea Anemone Nematostella vectensis. PloS one. Retrieved from https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086084.g002
Toyoda, H., Saito, M., Sato, H., & Tanaka, T. (2014). Enhanced desensitization followed by unusual resensitization in GABAA receptors in phospholipase C-related catalytically inactive protein-1/2 double-knockout mice. … -European Journal of …. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00424-014-1511-5
Wang, X., & Piñol, R. (2014). Optogenetic Stimulation of Locus Ceruleus Neurons Augments Inhibitory Transmission to Parasympathetic Cardiac Vagal Neurons via Activation of Brainstem α1 and. The Journal of …. Retrieved from https://www.jneurosci.org/content/34/18/6182.short


.1.png)














Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print