

M3301R
Manual Micromanipulator (right-handed)
- Overview
- Specifications
- Accessories
- Citations
- Related Products
Overview


There are 2 images available to view - click to enlarge and scroll through the product gallery.
Micromanipulator Care
/ Download as PDF
M3301 Drift adjustment sheet
/ Download as PDF
- Sure, repeatable movement without drift
- Vernier scales allow readings to 0.1mm & x-axis fine control allows readings to 10 μm
- Control knobs project to rear and are located in same vertical plane
- Tool holder suitable for handle diameter down to 6.4 mm OD
- Lightweight (550 g)
The world's most widely used micromanipulator
The M3301 manipulator outsells all others worldwide for high precision experiments where magnification is in the range of up to 250x.
The M3301 is a popular Manual Micromanipulator, because it is accurate, well-engineered and lightweight, at just 550 g. It's solid micromanipulator design delivers smooth, repeatable movements without drift. It has a slim, space-saving design. Units can stand tightly grouped, as all control knobs project to the rear. Resolution is quick because the control knobs are clustered within an 8 cm area in a single vertical plane. The hand works blindly while the eye monitors the microscopic image. Vernier scales allow readings to 0.1 mm. x-axis fine control allows readings to 10μm.
The instrument employs rack-and-pinion drive, v-shaped guideways, and cross roller bearings, so all movement is sure and repeatable, without drift, sideplay, backlash, or sticking. Contact parts are milled of hardened steel for high performance and long life. Left- or right-handed versions of the M3301 are supplied with a standard 12 mm clamp (M2) and one microelectrode holder (M3301EH). To complete the setup order stand or base separately (M10 Magnetic Stand, M-3 tilting base stand, M4C Microscope Stage Adapter)
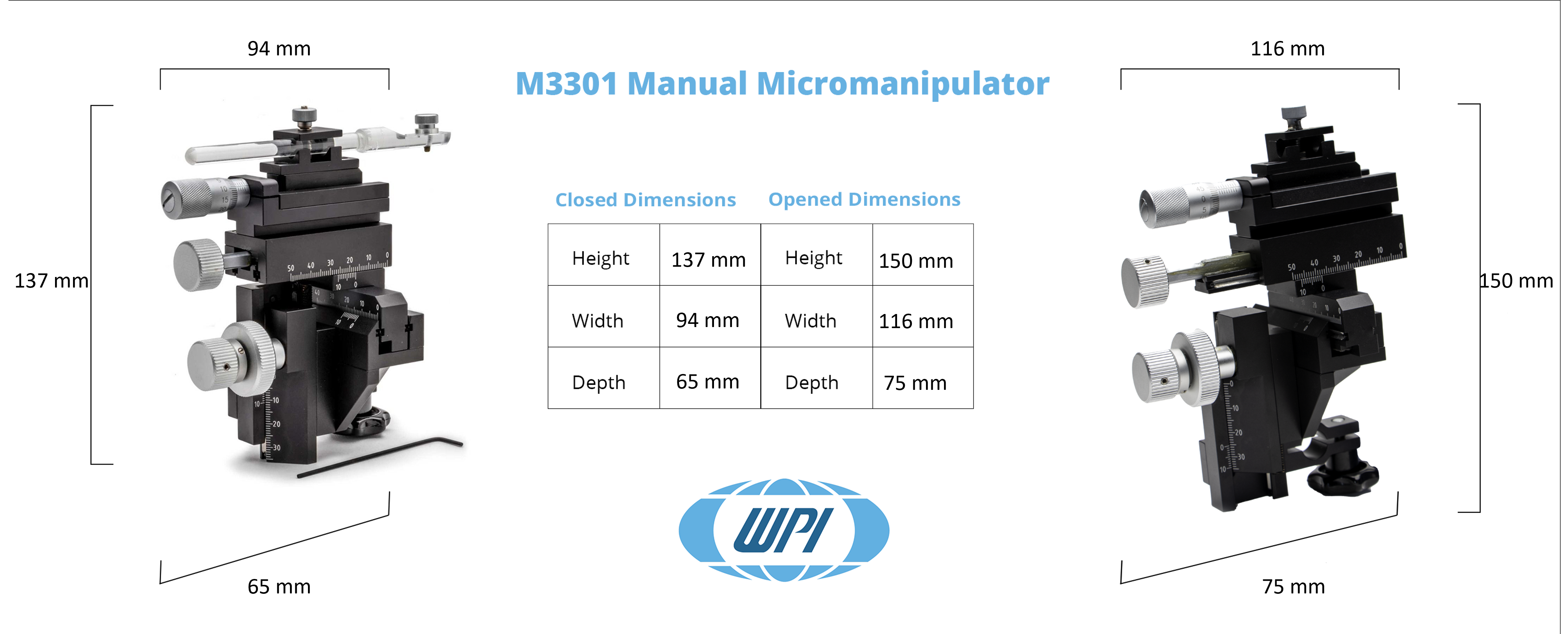
Specifications
| Travel Range: X-axis Fine | 10 mm |
| Travel Range: X-axis | 37 mm |
| Travel Range: Y-axis | 20 mm |
| Travel Range: Z-axis | 25 mm |
| Resolution: X-axis Fine | 0.01 |
| Resolution: X-axis | 0.1 mm |
| Resolution: Y-axis | 0.1 mm |
| Resolution: Z-axis | 0.1 mm |
| Shipping Weight: | 1.4 kg |
Accessories

M3301EH
Replacement Electrode Holder, 14 cm x 7.2 mm diameter.
Replacement Electrode f...
Citations
Bryant, L., Little, J., & Bürgmann, H. (2012). Response of sediment microbial community structure in a freshwater reservoir to manipulations in oxygen availability. FEMS microbiology ecology. Retrieved from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2011.01290.x/full
Chernet, B., Adams, D., & Levin, M. (2012). Photoconversion for Tracking the Dynamics of Cell Movement in Xenopus laevis Embryos. Cold Spring Harbor …. Retrieved from https://cshprotocols.cshlp.org/content/2012/6/pdb.prot068502.short
Chernet, B., & Levin, M. (2012). A Versatile Protocol for mRNA Electroporation of Xenopus laevis Embryos. Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. Retrieved from https://cshprotocols.cshlp.org/content/2012/4/pdb.prot067694.short
Gharbaran, R., & Aisemberg, G. (2012). Identification of leech embryonic neurons that express a Hox gene required for the differentiation of a paired, segment-specific motor neuron. International Journal of Developmental …. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0736574812005953
Laude, N., Atcherley, C., & Heien, M. (2012). Rethinking Data Collection and Signal Processing. 1. Real-Time Oversampling Filter for Chemical Measurements. Analytical chemistry. Retrieved from https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac302169y
Luetje, C., Nichols, A., Castro, A., & Sherman, B. (2013). Functional Assay of Mammalian and Insect Olfactory Receptors Using Xenopus Oocytes. Olfactory Receptors. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/protocol/10.1007/978-1-62703-377-0_14
Wang, Y., Shah, P., & Phillips, C. (2012). Trapping cells on a stretchable microwell array for single-cell analysis. Analytical and …. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00216-011-5535-9
Zeeb, M. (2013). Whole-embryo culture of mouse embryos to study vascular development. Retrieved from https://docserv.uni-duesseldorf.de/servlets/DerivateServlet/Derivate-26166/PhDThesis_MartinZeeb.pdf
Zeeb, M., Axnick, J., Planas-Paz, L., & Hartmann, T. (2012). Pharmacological manipulation of blood and lymphatic vascularization in ex vivo–cultured mouse embryos. Nature protocols. Retrieved from https://www.nature.com/nprot/journal/v7/n11/abs/nprot.2012.120.html


.png)








Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print