
Zebra Fish Microinjection
Instruments for Zebrafish research - oocytes, embryos, larvae and adults
World Precision Instruments (WPI) offers a broad range of research instruments for zebrafish (Danio Rerio) research, from the time the genetics of the subject are modified through the point where the physiological effects of the change are monitored. Whether researchers are performing microinjection or making cardiovascular measurements, the WPI product line includes instruments for research on oocytes, embryos, larvae and adult zebrafish.

Enhanced microinjection efficiency for genetic modification
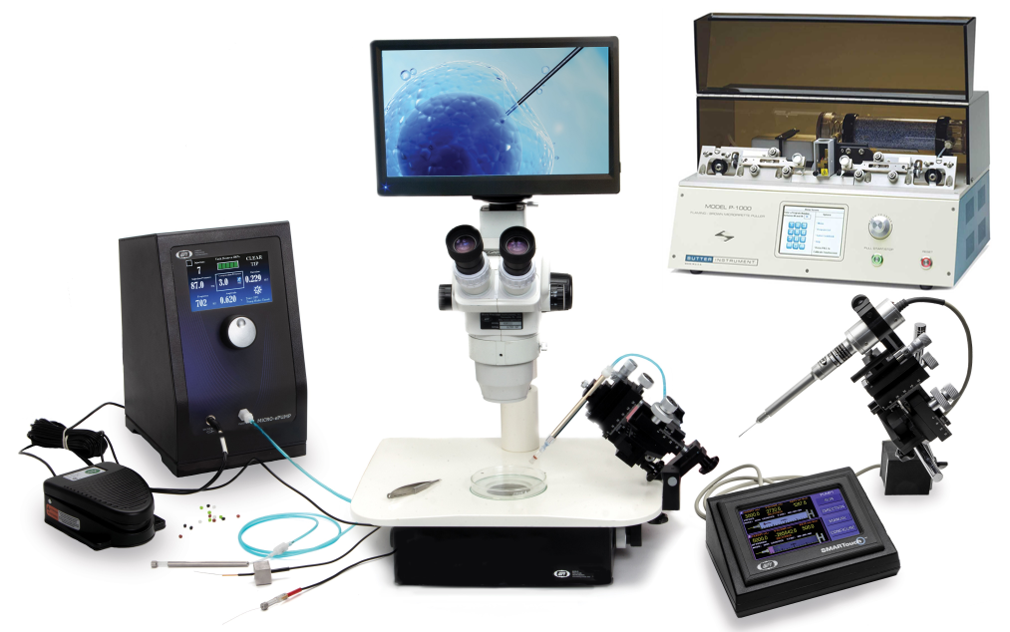

The customizable Zebrafish Microinjection Toolbox includes components favored by researchers: MICRO-ePUMP Pneumatic PicoPump with built in MICRO-ePORE™ Cell Penetrator to facilitate microinjections, P-1000 Micropipette Puller, PZMTIII-MI/PZMIII-MI Trinocular or Binocular Microscope on lighted base with articulating mirror, PRO-300HDS High Definition Camera and Monitoring System, and accessories.
The NANOLITER2020 Injector and the UMP3T-1 UltraMicroPump with SMARTouch Touchscreen Controller are alternate injectors. WPI has been serving scientists for over 50 years with easy and cost-effective tools for genetic modification. WPI offers a wide range of instruments required for microinjection of zebrafish in oocytes (ref 1), embryo (ref 1), larvae (ref 3) and adults (ref 4) to enable genetic modification.
Direct cardiovascular measurements for embryos, larvae and adult fish
Embryonic zebrafish have become a popular model for cardiovascular research (ref 5). WPI is a pioneer in developing instruments for research in electrophysiology and is cited in 1000s of peer-reviewed publications. WPI introduced the CardioPhys™ Z series of products that makes measurement of cardiovascular functionalities in zebrafish embryo easy.
WPI CardioPhys™ Z ECG (prototype)
The novel WPI CardioPhys™ Z ECG allows direct measurement of ECG in zebrafish embryos. WPI has optimized its existing electrophysiology product line to meet the demands of the zebrafish researcher.

- Ensures very low noise for recording electrical activity of zebrafish embryonic heart
- High resistance to environmental electrical noise
- User-friendly software
- Allows researchers to identify diagnostic indices of cardiovascular physiology such as altered rhythm, signal conduction abnormalities, damage from cardiac events such as ischemia and infarction, etc.
CardioPhys™ Z BP (prototype)
The new WPI CardioPhys™ Z BP is designed to record hydrostatic pressure in very small vessels using a Servo-Null system (ref 6) The system has been used to measure blood pressure in the Zebrafish (embryo, larvae and adult fish) with less than 0.5 mmHg resolution.
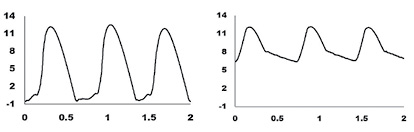
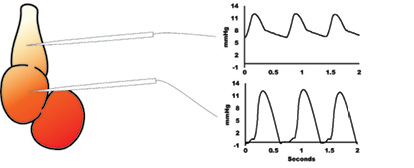
Pressure signal from the WPI CardioPhys™ Z BP from the ventricle (top) and bulbus arteriosis (bottom) in a larva.
Detection of free radicals & other molecules for disease models

This is a typical laboratory setup of a WPI free radical analyzer with data acquisition system.
The WPI Free Radical Analyzer, TBR4100, enables real-time, highly sensitive detection of free radicals such as NO, H2O2, H2S, CO, O2–important physiological indicators in intracellular cell signaling and homeostasis. Free radicals beyond the level of normal detoxication can result in oxidative stress (OS).7 OS affects wound healing and aging, and it causes several diseases such as diabetes mellitus, neurodegenerative disorders (Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and Multiple sclerosis), cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis and hypertension), respiratory diseases (asthma), cataract development, rheumatoid arthritis and various cancers (colorectal, prostate, breast, lung, bladder cancers) (ref 8)
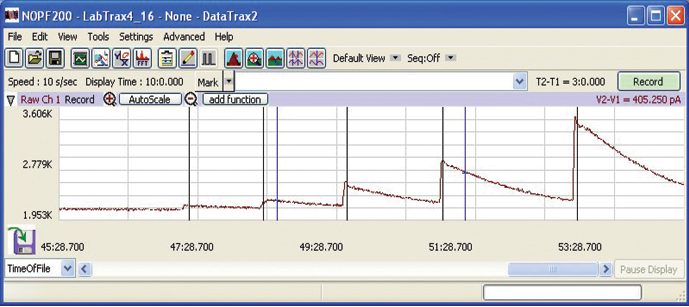
The output shows the raw data for an ISO-NOPF200 (NO sensor). Only one of the four channels is used in this application.
References
- Eric S. Clelland, Qian Tan, Ari Balofsky, Rosie Lacivita, Chun Peng. Inhibition of Premature Oocyte Maturation: A Role for Bone Morphogenetic Protein 15 in Zebrafish Ovarian Follicles. Endocrinology, Volume 148, Issue 11, 1 November 2007, Pages 5451–5458,https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-0674
- Rosen JN, Sweeney MF, Mably JD. Microinjection of zebrafish embryos to analyze gene function. J Vis Exp. 2009 Mar 9;(25). pii: 1115. doi: 10.3791/1115.
- Cianciolo Cosentino, C., Roman, B. L., Drummond, I. A., Hukriede, N. A. Intravenous Microinjections of Zebrafish Larvae to Study Acute Kidney Injury. J. Vis. Exp. (42), e2079, doi:10.3791/2079 (2010).
- Kinkel, M. D., Eames, S. C., Philipson, L. H., Prince, V. E. Intraperitoneal Injection into Adult Zebrafish. J. Vis. Exp. (42), e2126, doi:10.3791/2126 (2010).
- Staudt, D. & Stainier, D. Uncovering the molecular and cellular mechanisms of heart development using the zebrafish. Annu Rev Genet 46, 397–418 (2012).
- Hu N1, Yost HJ, Clark EB. Cardiac morphology and blood pressure in the adult zebrafish. Anat Rec. 2001 Sep 1;264(1):1-12.
- Katerji M1, Filippova M1, Duerksen-Hughes P1. Approaches and Methods to Measure Oxidative Stress in Clinical Samples: Research Applications in the Cancer Field. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Mar 12;2019:1279250. doi: 10.1155/2019/1279250. eCollection 2019.
- Alugoju Phaniendra, Dinesh Babu Jestadi, and Latha Periyasamy. Free Radicals: Properties, Sources, Targets, and Their Implication in Various Diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2015 Jan; 30(1): 11–26.

PZMIII-MI
Binocular Stereo Microscope with LED Illuminated Base and Articulating Mirror

PZMTIII-MI
Trinocular Stereo Microscope with LED Illuminated Base and Articulating Mirror

Nanoliter2020 Injector
Precise nanoliter-volume injections using glass with intuitive SMARTouch™ cont...

Z-MOLDS
Zebrafish Microinjection and Transplantation Molds - organizes and immobilizes embry...












Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print