

SPLG180
Legato 180 Dual Syringe I/W Programmable
- Overview
- Specifications
- Accessories
- Citations
- Related Products
Overview
Features:
- Holds one or two syringes from 0.5ul to 10ml
- High resolution color touch screen
- Unparalled ease of use
- Touch pad "lock" feature
- LED light on front panel
- Full metal chassis
- Built in syringe table
- Up to 30 lbs linear force
- Advanced microstepping techniques
- Built in RS485 interface
- USB port
- I/O & TTL interface
- Continuous mode of operation
- Spill dam
- Programmable
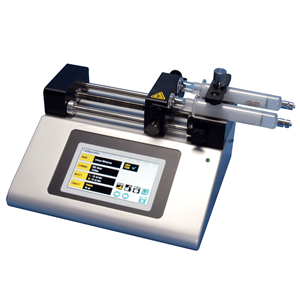
The SPLG180 Pico pump has infusion and withdrawal capabilities with accurate deliveries of picoliter, nanoliter, microliter and milliliter flow. It is especially designed to hold microliter syringes ranging from 0.5ul to 10ml.
The Pico pump will operate continuously in “rate” mode or accurately dispense a specific amount of fluid in “volume” mode. The microstepping pump delivers very smooth and constant flow over the entire flow range. The Pico pump feature non-volatile memory. The pump remembers its last syringe size, flow rate and configuration settings.
Dual syringe infuse/withdraw optimized for low flow with program options for 2 programs. 50 steps each. Accomodates syringes 0.5ul to 10ml. User definable flow rates with selectable target volume or time values to control the total infusion volume.
Examples of flowrates
| Syringe | Diameter | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 µl | 0.103 mm | 0.540 pl/min | 596.20 nl/min |
| 1 µl | 0.146 mm | 1.140 pl/min | 1.193 µl/min |
| 2 µl | 0.206 mm | 2.280 pl/min | 2.385 µl/min |
| 5 µl | 0.343 mm | 6.360 pl/min | 6.612 µl/min |
| 10 µl | 0.485 mm | 12.720 pl/min | 13.220 µl/min |
| 25 µl | 0.729 mm | 28.740 pl/min | 29.870 µl/min |
| 50 µl | 1.03 mm | 57.360 pl/min | 59.620 µl/min |
| 100 µl | 1.457 mm | 114.800 pl/min | 119.300 µl/min |
| 250 µl | 2.304 mm | 287.200 pl/min | 298.300 µl/min |
| 500 µl | 3.256 mm | 573.700 pl/min | 595.800 µl/min |
| 1000 µl | 4.608 mm | 1.149 nl/min | 1.193 ml/min |
| 1 ml | 4.699 mm | 1.195 nl/min | 1.241 ml/min |
| 3 ml | 8.585 mm | 3.988 nl/min | 4.142 ml/min |
| 5 ml | 11.989 mm | 7.778 nl/min | 8.078 ml/min |
| 10 ml | 14.427 mm | 11.260 nl/min | 11.700 ml/min |
Specifications
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
Accuracy: |
± 0.35% |
Reproducibility |
± 0.05% |
Syringes (Min/Max) |
0.5 ul to 10ml |
Flow Rate: |
Minimum (0.5 ul syringe): 0.58 pl/min Maximum (10ml syringe): 11.70 ml/min |
Display |
4.3 WQVGA TFT Color Display with Touchpad |
Non-Volatile Memory |
Stores all Settings |
Connectors: |
RS485 - IEEE-1394 6 pos USB - Type B I/O & TTL - 15 pin D-Sub Connector |
Linear Force (Max) |
13.6 kg (30 lbs) @ 100% Force Selection |
Drive Motor |
0.9 Stepper Motor |
Motor Drive Control |
Microprocessor with 1/16 microstepping |
Number of Microstepsper one rev.of Lead Screw |
20,480 |
Step Revolution |
0.031 um/ustep |
Step Rate - Minimum |
27.5 sec/ustep |
Step Rate - Maximum |
26 usec/ustep |
Pusher Travel Rate - Minimum |
0.02 um/min |
Pusher Travel Rate - Maximum |
71.55 mm/min |
Power |
100-240 VAC: 50/60 Hz, 50 W, 0.5 A fuse |
Dimensions |
22.6 x 19.05 x 15 cm (9 x 7.5 x 5 in) |
Weight |
2.66 kg (5.9 lbs) |
Operating Temperature |
4 degree C to 40 degree C (40 degree F to 104 degree F) |
Storage Temperature |
-10 degree C to 70 degree C (14 degree F to 158 degree F) |
Humidity |
20% to 80% RH non condensing |
Mode of Operation |
Continuous |
Classification |
Class 1 |
Pollution Degree |
1 |
Installation Category |
11 |
Regulatory Certification |
CE, UL, CSA, CB Scheme, EU RoHS |
Accessories
Citations
Gunaratne, K., & Prabhakaran, V. (2015). Design and performance of a high-flux electrospray ionization source for ion soft landing. Analyst. Retrieved from https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2015/an/c5an00220f
Horvath, C., Arratia, C., & Cordero, M. (2015). Measurement of the dispersion relation of a convectively unstable capillary jet under confinement. Physics of Fluids (1994-Present). Retrieved from https://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/pof2/27/11/10.1063/1.4935699
Khalili, A. A., & Ahmad, M. (2016). A Microfluidic Device for Hydrodynamic Trapping and Manipulation Platform of a Single Biological Cell. Applied Sciences. Retrieved from https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/6/2/40/htm
Kidd, R., Noell, A., & Kazarians, G. (2015). Ion Chromatography-on-a-Chip for Water Quality Analysis. Retrieved from https://ttu-ir.tdl.org/ttu-ir/handle/2346/64414
Kim, J., & Szinte, J. (2016). 17β-Estradiol and Agonism of G-protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor Enhance Hippocampal Memory via Different Cell-Signaling Mechanisms. The Journal of …. Retrieved from https://www.jneurosci.org/content/36/11/3309.short
Lin, Y., & Peng, P. (2015). Semiconductor sensor embedded microfluidic chip for protein biomarker detection using a bead-based immunoassay combined with deoxyribonucleic acid strand. Analytica Chimica Acta. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003267015002937
Shen, Z., Coupier, G., Kaoui, B., & Polack, B. (2016). Inversion of hematocrit partition at microfluidic bifurcations. Microvascular …. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0026286215300479
Xue, P., Wu, Y., Guo, J., & Kang, Y. (2015). Highly efficient capture and harvest of circulating tumor cells on a microfluidic chip integrated with herringbone and micropost arrays. Biomedical Microdevices. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10544-015-9945-x
Xue, P., Wu, Y., Menon, N., & Kang, Y. (2015). Microfluidic synthesis of monodisperse PEGDA microbeads for sustained release of 5-fluorouracil. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10404-014-1436-5
Yoshida, K., & Onoe, H. (2015). Self-assembled hydrogel microspring for soft actuator. Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS …. Retrieved from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=7050877
RelatedItems

SPLG270
Legato 270 Push/Pull Syringe Pump (four syringes - two syringes for infusion, two sy...

SPLG272
Legato 272 Programmable Push/Pull Syringe Pump (four syringes - two syringes for inf...










Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print