

MCTR
MechanoCulture MCTR – 9 specimen hydrostatic stimulation
- Overview
- Specifications
- Accessories
- Citations
- Related Products
Overview
High throughput hydrostatic pressure stimulation
The MCTR provides hydrostatic compression to 9 specimens in individual wells. Pressure up to 500 kPa can be programmed onto the device. The transparent culture wells allow for visual confirmation of correct specimen loading and real-time imaging during the test if desired. The specimen chamber plate can be sterilized and the system is suitable for long-term cell culture in a laboratory incubator.
Key Features
- Hydrostatic compression stimulation for up to 9 culture wells
- Pressure-controlled loading up to 500kPa at 0.5Hz
- User-friendly interface software for specifying simple, cyclic, and intermittent stimulation protocols for upload to the device controller
HydroStatic Compression
Hydrostatic compression is achieved by filling the culture well to the top with media. Pressurizing the top chamber results in the flexible membrane deflecting downwards to press against the surface of the liquid.
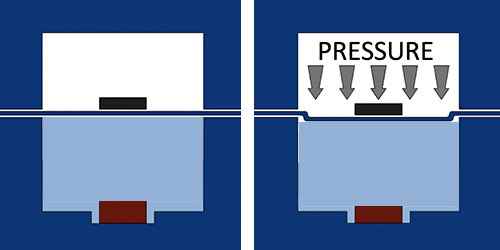
MCTR Hydrostatic Demonstration
Specifications
| Dimensions | 14 x 14 x 9cm |
| Weight | 1kg |
| Stimulation Mode |
Hydrostatic Pressure Stimulation |
| Configuration | Constructs up to 20mm diameter/width |
| Maximum Pressure | 500kPa |
| Maximum Cycle Frequency | 0.5 Hz |
Accessories

MCT6-200
Mechanoculture T6 - High force uniaxial stimulation of 6 parallel specimens
Citations
Szojka, A., Li, D. X., Sopcak, M., Ma, Z., Kunze, M., Mulet-Sierra, A., Adeeb, S. M., Westover, L., Jomha, N. M., & Adesida, A. B. (2021). Mechano-Hypoxia Conditioning of Engineered Human Meniscus. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology vol. 9 739438. 3 Sep. 2021, doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.739438
Elena Cambria,Sally Heusser,Ariane C. Scheuren,Wai Kit Tam,Agnieszka A. Karol,Wolfgang Hitzl,Victor Y. Leung,Ralph Müller,Stephen J. Ferguson,Karin Wuertz-Kozak (2021). TRPV4 mediates cell damage induced by hyperphysiological compression and regulates COX2/PGE2 in intervertebral discs. JOR spine vol. 4,3 e1149. 6 May. 2021, doi:10.1002/jsp2.1149
C. Ludovica, G. Mattei, A. Ahluwalia (2020). A New Load-controlled Testing Method for Viscoelastic Characterisation Through Stress-rate Measurements. Materialia, Volume 9, 2020, 100552, ISSN 2589-1529
Cambria, E., Brunner, S., Heusser, S., Fisch, P., Hitzl, W., Ferguson, S.J. and Wuertz-Kozak, K. (2020). Cell-laden agarose-collagen composite hydrogels for mechanotransduction studies. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology vol. 8 346. 21 Apr. 2020, doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.00346
Sit, B., Feng, Z., Xanthis, I., Marhuenda, E., Zingaro, S., Shanahan, C., Jones, G., Yu, C.H. and Iskratsch, T. (2020). Matrix stiffness and blood pressure together regulate vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype switching and cofilin dependent podosome formation. bioRxiv 2020.12.27.424498;
C. Ludovica (2019). Advanced In-vitro Models with Integrated Sensing for Real-time Monitoring of Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Cellular Constructs.
A. Sensini, L. Christofolini, A. Zucchelli, M. L. Focarete, C. Gualandi, A. De Mori, A. P. Kao, M. Roldo, G. Blunn, G. Tozzi (2019). Hierarchical Electrospun Tendon-ligament Bioinspired Scaffolds Induce Changes in Fibroblasts Morphology under Static and Dynamic Conditions. Journal of microscopy vol. 277,3 (2020): 160-169. doi:10.1111/jmi.12827
RelatedItems

MCT6-200
Mechanoculture T6 - High force uniaxial stimulation of 6 parallel specimens
MCFX-400
DISCONTINUED - MechanoCulture FX , 16-well cell culture bioreactor with unaxial stre...

MCB1-200
MechanoCulture B1 - Biaxial stimulation of a cells in a monolayer or 3D matrix








Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print