

MCB1-200
MechanoCulture B1 - Biaxial stimulation of a cells in a monolayer or 3D matrix
- Overview
- Specifications
- Accessories
- Citations
- Related Products
Overview

There are 2 images available to view - click to enlarge and scroll through the product gallery.
Data Sheet
/ Download as PDF
-
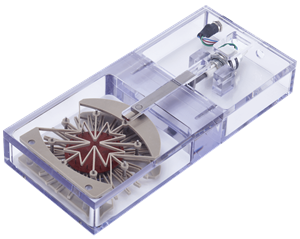
Biaxial stimulation of a cells in a monolayer or 3D matrix
The MCB1 uses a complex deformable interface to generate radial motion patterns on a 24-pin mounting ring. User-supplied 35mm diameter membranes, scaffolds, and tissues can be puncture-mounted to this ring and biaxially stretched according to the specified protocol. The entire assembly can be sterilized and is suitable for long-term cell culture in a laboratory incubator.
Key Features
- Biaxial stretch up to 20%
- Compatible with a wide range of materials including silicone membranes, decellularized tissues, hydrogels, electrospun materials, and more.
- PC-independent operation
- User-friendly interface software for specifying simple, cyclic, and intermittent stimulation protocols for download to the device controller
Specifications
| Dimensions | 22 X 10 X 4cm |
| Weight | 1 kg |
| Stimulation Mode | Biaxial tension |
| Configuration | Cell monolayer, 3D constructs and tissues |
| Culture Area | 1 well, 35mm diameter |
| Maximum Strain | 20% biaxial |
| Maximum Velocity | 10mm/s |
| Maximum Cycle Frequency | 2Hz |
| Loading Capacity | 10N |
| Media Volume/well | 0.5-100mL |
Accessories
Citations
Rashika Joshi, Matthew R. Batie, Qiang Fan, and Brian Michael Varisco* (2021). Mouse Lung Organoid Responses to Reduced, Increased, and Cyclic Stretch. American journal of physiology. Lung cellular and molecular physiology vol. 322,1 (2022): L162-L173. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00310.2020
Xun Xu, Yan Nie, Weiwei Wang, Nan Ma & Andreas Lendlein (2021). Periodic thermomechanical modulation of toll-like receptor expression and distribution in mesenchymal stromal cells. MRS communications, 1-7. 8 Jul. 2021, doi:10.1557/s43579-021-00049-5
Kim, M.K.M., Burns, M.J., Serjeant, M.E. and Séguin, C.A., (2020). The mechano-response of murine annulus fibrosus cells to cyclic tensile strain is frequency dependent. JOR spine vol. 3,4 e21114. 20 Jul. 2020, doi:10.1002/jsp2.1114
O. Friedrich, A-L. Merten, D. Schneidereit, Y. Guo, S. Schurmann, N. Martinac (2019). Stretch In Focus: 2d Inplane Cell Stretch Systems For Studies Of Cardiac Mechano-Signaling. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology vol. 7 55. 27 Mar. 2019, doi:10.3389/fbioe.2019.00055
K. Chen, A. Vigliotti, M. Bacca, R. M. McMeeking, V.S. Dashpande, J.W. Holmes (2018). Role Of Boundary Conditions In Determining Cell Alignment In Response To Stretch. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America vol. 115,5 (2018): 986-991. doi:10.1073/pnas.1715059115
RelatedItems

MCT6-200
Mechanoculture T6 - High force uniaxial stimulation of 6 parallel specimens
MCFX-400
DISCONTINUED - MechanoCulture FX , 16-well cell culture bioreactor with unaxial stre...

MCB1-200
MechanoCulture B1 - Biaxial stimulation of a cells in a monolayer or 3D matrix






Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print