

UMP3T-2
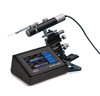
Two UltraMicroPump3 (UMP3) pump heads with SMARTouch Controller
- Overview
- Specifications
- Accessories
- Citations
- Related Products
Overview




There are 4 images available to view - click to enlarge and scroll through the product gallery.
UMP3 with MICRO2T Manual
/ Download as PDF
Quick Start Guide For UMP3 with MICRO2T
/ Download as PDF
- Graphic display with SMARTouch™ touch screen controller for "intelligent", easy to use interface controlling up to two syringe pumps
- Splash proof touch screen
- User configurable mounting bar
- Dual mode motor drive
- Compatible with all UMP, UMP2 and UMP3 pumps
- Optional foot switch available
- 5 digit display
Benefits
- Accepts a wide variety of microinjection syringes
- Manual or automated injections
- Quiet operation for electrophysiology recordings
- Mounts directly on micromanipulator or stereotaxic frame
- Nominal injections down to 1nL
- Rapid setup with intuitive touchscreen controller
Applications
- Microinjection
- Neuroscience
- Microfluidics
- Micro delivery of biochemical agents or dyes
The UltraMicroPump3 (UMP3) is a versatile pump which uses micro syringes to deliver picoliter to milliliter volumes. The pump is optimum for applications that require injections of precise and small amounts of liquid. With its touchscreen controller, UMP3 can displace as little as 0.53 µL/step (using 10 µL syringe with 60 mm scale length).
Patent Pending technology
The new SMARTouch™ controller for the UltraMicroPump3 features Patent Pending technology which includes:
- Total system calibration – Calibrate the syringe and the controller together as a system. This feature eliminates the variability of the syringes and delivers the calibrated volume.
- Smart smoothness – The controller can be set to automatically adjust microstepping according to the injection rate to deliver the smoothest flow.
- User defined travel limits – Set the limits for a specific syringe in the software. This prevents the pump from over-driving the plunger into the syringe, potentially causing syringe breakage.
The MICRO2T SMARTouch™ controller is feature rich. All operations are controlled through interactive touch screen. It has a graphical indication of the flow and the volume remaining in the syringe. It offers end stop detection that is dependent on the syringe volume. You can control two pumps independently from one controller with its dual display. It also has automatic pump detection and a Pause/Resume feature that allows dosing during infusion/withdrawal. The volume accumulated is displayed on screen, as well as the percentage of volume left in the syringe. The SMARTouch™ controller is fully compatible with all earlier versions of the UltraMicroPump.
Low Fluid Dead Volume
Syringes may be filled externally and then inserted into the pump or filled while mounted in the pump. Fluids injected or withdrawn are held entirely within the micro syringe to maintain a low fluid dead volume.
Flexibility in Mounting
For positioning, the UMP3 may be attached to any of several WPI micropositioners such as the M3301 (manual), DC3001 (motorized) or any manual stereotaxic manipulator.
Rapid Setup with Intuitive Touchscreen Controller
An Integral component in the UMP3 system is the SMARTouch™ touchscreen controller, which provides an “intelligent” and easy-to-use interface up to two syringe pumps. Operating parameters are set with the touchscreen panel. An optional footswitch offers “hands free” start/stop operation.
Computer Control—A USB port on the rear of the controller can be used to connect it to a computer for scripted protocols.
NOTE: UMP3 accepts glass syringes with barrel diameters from 5.5 to 9 mm.
Specifications
Ultramicropump specifications
(based on 10 μL syringe)
|
Normal Mode |
|
|
Travel |
62 mm |
|
Minimum dispensing volume |
0.58 nL / step (10 µL syringe) |
|
Linear motion per step |
3.175 µm/half step |
|
Weight |
325 g (11.5 oz) |
|
Mounting rod diameters |
7.9 mm (0.31 in.) |
|
Mains power supply |
90-264VAC @ 47-63Hz |
|
Dimensions |
∅ 32 mm x 190 mm (∅ 1.3 in. x 7.5 in.) |
|
Microstepping Mode |
|
|
Precision is increased eight-fold. |
Accessories
502201
V-Clamp Attachment for UMP3. Attach the UMPIII UltraMicroPump to the stereotaxic fra...
Citations
Zhou, Z., Luther, N., Singh, R., Boockvar, J. A., Souweidane, M. M., & Greenfield, J. P. (2017). Glioblastoma spheroids produce infiltrative gliomas in the rat brainstem. Child’s Nervous System, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3344-y
Ye, H.-L., Li, D.-R., Yang, J.-S., Chen, D.-F., De Vos, S., Vuylsteke, M., … Yang, W.-J. (2017). Molecular characterization and functional analyses of a diapause hormone receptor-like gene in parthenogenetic Artemia. Peptides. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2017.01.008
Wofford, K. L., Harris, J. P., Browne, K. D., Brown, D. P., Grovola, M. R., Mietus, C. J., … Cullen, D. K. (2017). Rapid neuroinflammatory response localized to injured neurons after diffuse traumatic brain injury in swine. Experimental Neurology, 290, 85–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.01.004
Qi, Y., Purtell, L., Fu, M., Zhang, L., Zolotukhin, S., Campbell, L., & Herzog, H. (2017). Hypothalamus specific re-introduction of Snord116 into otherwise Snord116 deficient mice increased energy expenditure. Journal of Neuroendocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12457
Mosberger, A. C., Miehlbradt, J. C., Bjelopoljak, N., Schneider, M. P., Wahl, A.-S., Ineichen, B. V., … Schwab, M. E. (2017). Axotomized Corticospinal Neurons Increase Supra-Lesional Innervation and Remain Crucial for Skilled Reaching after Bilateral Pyramidotomy. Cerebral Cortex, 137, 1716–1732. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhw405
Job, M. O., & Kuhar, M. J. (2017). CART peptide in the nucleus accumbens regulates psychostimulants: Correlations between psychostimulant and CART peptide effects. Neuroscience, 348, 135–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.02.012
Eleftheriadou, I., Dieringer, M., Poh, X. Y., Sanchez-Garrido, J., Gao, Y., Sgourou, A., … Mazarakis, N. D. (2017). Selective transduction of astrocytic and neuronal CNS subpopulations by lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with Chikungunya virus envelope. Biomaterials, 123, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.01.023
Augestad, I. L., Nyman, A. K. G., Costa, A. I., Barnett, S. C., Sandvig, A., Håberg, A. K., & Sandvig, I. (2017). Effects of Neural Stem Cell and Olfactory Ensheathing Cell Co-transplants on Tissue Remodelling After Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia in the Adult Rat. Neurochemical Research, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2098-3









Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print