

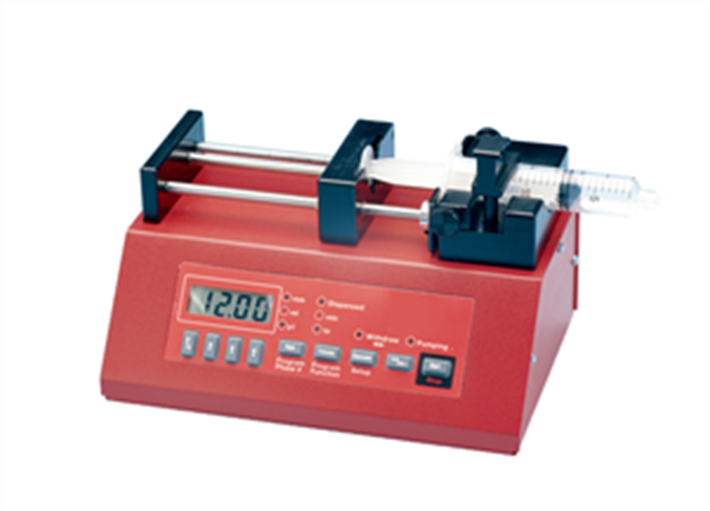
OXY-MICRO-AOT
Fiber Optic Oxygen Meter for Microsensors
- Overview
- Specifications
- Accessories
- Citations
- Related Products
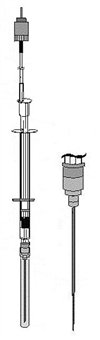
Overview

There are 1 images available to view - click to enlarge and scroll through the product gallery.
OxyMicro Datasheet
/ Download as PDF
OxyMicro Instruction Manual
/ Download as PDF
- Detection based on luminescence lifetime
- Excellent long-term stability
- Fast response time (< 0.5 sec for MicroTip sensors)
- Measurement is feasible in dry gas
- Immune to electrical and magnetic interference
Features
The OxyMicro is designed for biological research applications including implanting into tissues, cell cultures, profiling of biofilms and sediment related bioassays. The measurement principle of the sensor system is based on the detection of oxygen concentration as a function of luminescence lifetime either in dissolved or gaseous phase environments. The fiber optic oxygen meter is compact and easy to transport. It was designed for in/outdoor use and can be connected to a PC via a RS232 interface. Data can be visualized, analyzed and stored with the supplied software. A full range of sensors covering most biomedical applications are available.
Measurement Principle
Conventional fiber-optic oxygen sensor systems based on intensity measurements are limited in their accuracy by light source stability and ambient light fluctuations. Using a luminescence lifetime detection, measurements are not affected by light source stability, intensity fluctuations caused by fiber bending or changes of the optical properties of the sample (turbidity, refractive index, coloration, etc.). These advantages make WPI™s OxyMini and OxyMicro the most advanced and reliable fiber-optic oxygen system available.
Calibration
The sensors can be calibrated by a simple two point calibration, 100% air-saturation and 0% air saturation.
Applications
The OxyMicro is a single channel fiber optic oxygen meter for WPI™s fiber optic oxygen microsensors. Applications include:
- Oxygen profiles of marine sediment, soils, or tissue
- Implantation into living tissue (e.g., heart or muscle tissue)
- Control of cell culture media in Biotechnology.
Specifications
Accessories

501657
MicroFlow - Flow-through housed oxygen microsensor for use with OXY-MICRO-AOT
Citations
Chai, W., Dong, Z., Wang, N., Wang, W., & Tao, L. (2012). Glucagon-like peptide 1 recruits microvasculature and increases glucose use in muscle via a nitric oxide–dependent mechanism. Diabetes. Retrieved from https://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/61/4/888.short
Gandra, P. (2012). Mitochondrial activation at the onset of contractions in isolated myofibres during successive contractile periods. The Journal of Physiology. Retrieved from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1113/jphysiol.2012.232405/full
Larsson, C., Luna, B., & Ammerman, N. (2012). Gene expression of Mycobacterium tuberculosis putative transcription factors whiB1-7 in redox environments. PloS one. Retrieved from https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037516
Li, C., Wu, Z., & Hartings, J. (2012). Brain-friendly amperometric enzyme biosensor based on encapsulated oxygen generating biomaterial. … in Medicine and …. Retrieved from https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=6347362
Radhakrishnan, N., Park, J., & Kim, C. (2012). An Oxidase-Based Electrochemical Fluidic Sensor with High-Sensitivity and Low-Interference by On-Chip Oxygen Manipulation. Sensors. Retrieved from https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/12/7/8955/pdf
Shapiro, R., Barr, B., Putnam, R., & Wyatt, C. (2012). Acute Hypoxia Does Not Influence Intracellular pH in Isolated Rat Carotid Body Type I Cells. Arterial Chemoreception. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-007-4584-1_14




Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print