
ECGenie
Awake Lab Animal ECG System- Overview
- Specifications
- Accessories
- Citations
- Related Products
Overview
There are 1 images available to view - click to enlarge and scroll through the product gallery.
ECGenie Specifications
/ Download as PDF
Recording and Analysis Overview
/ Download as PDF
EzCG Analyses software features
/ Download as PDF
The ECGenie is a rapid non-invasive solution for recording electrocardiograms (ECGs) in awake mice, rats, and guinea pigs. Applications include arrhythmia detection, health monitoring, and drug screening in fragile transgenic and knockout animals, including newborn pups.
ECGenie records the cardiac electrical signals at 2 kHz to provide optimal fidelity in describing the rapid ECG interval durations in mice (e.g., a QRS interval duration of ~8 ms). The typical laboratory setting easily accommodates the footprint of the entire system. This includes the shielded acquisition platform, analog input and bioamplification, and direct connection to Windows and MacOS computers.
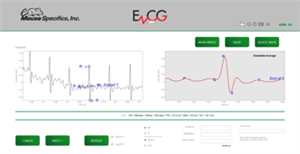
The instrument is based on patented technology for non-invasively detecting cardiac electrical activity through the animals’ paws. The size and spacing of disposable footplate electrodes facilitate contact between the electrodes and the paws to provide a lead II ECG in laboratory animals. EzCG analyses software, provided by Mouse Specifics, analyzes the signals to assess animal health, cardiac diseases, and drug toxicity.
ECGenie features:
- “Quick-connect” interchangeable platforms for mice and larger rodents
- Disposable footplate electrodes
- High-pass and low-pass filtering
- SCSI and USB interface for connection to Windows and MacOS computers
NO Anesthetic • NO Implants • NO Surgery
EzCG Analyses software features
- Interpretation of ECGs from conscious moving mice, rats, and guinea pigs
- Published algorithms for heart rate and P Q R S T interval durations
- Custom inclusion of client-specific algorithms, including QTc
- HTML and text formatted output for multiple spreadsheet applications
Specifications
Accessories
Citations
Monroe, L. L., Armstrong, M. G., Zhang, X., Hall, J. V., Ozment, T. R., Li, C., … Hoover, D. B. (2016). Zymosan-Induced Peritonitis. SHOCK, 46(6), 723–730. http://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000669
Reduction of thalamic and cortical Ih by deletion of TRIP8b produces a mouse model of human absence epilepsy. (2016). Neurobiology of Disease, 85, 81–92. http://doi.org/10.1016/J.NBD.2015.10.005
Gatti, D. M., Simecek, P., Somes, L., Jeffery, C. T., Vincent, M. J., Choi, K., … Svenson, K. L. (2017). The Effects of Sex and Diet on Physiology and Liver Gene Expression in Diversity Outbred Mice. Doi.org, 98657. http://doi.org/10.1101/098657
Erickson, R. L., Terzi, M. C., Jaber, S. M., Hankenson, F. C., McKinstry-Wu, A., Kelz, M. B., & Marx, J. O. (n.d.). Intraperitoneal Continuous-Rate Infusion for the Maintenance of Anesthesia in Laboratory Mice (Mus musculus). Retrieved from http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/aalas/jaalas/2016/00000055/00000005/art00007
Effect and mechanism of Irbesartan on occurrence of ventricular arrhythmias in rats with myocardial ischemia through connexin43 (cx43). (2016). Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, 9(10), 1007–1012. http://doi.org/10.1016/J.APJTM.2016.07.022
Zimmers, T. A., Jiang, Y., Wang, M., Liang, T. W., Rupert, J. E., Au, E. D., … Koniaris, L. G. (2017). Exogenous GDF11 induces cardiac and skeletal muscle dysfunction and wasting. Basic Research in Cardiology, 112(4), 48. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-017-0639-9
Giudice, J., Xia, Z., Li, W., & Cooper, T. A. (2016). Neonatal cardiac dysfunction and transcriptome changes caused by the absence of Celf1. Scientific Reports, 6, 35550. http://doi.org/10.1038/srep35550
Downs, A. M., Jalloh, H. B., Prater, K. J., Fregoso, S. P., Bond, C. E., Hampton, T. G., & Hoover, D. B. (2016). Deletion of neurturin impairs development of cholinergic nerves and heart rate control in postnatal mouse hearts. Physiological Reports, 4(9), e12779. http://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.12779
de Souza Dyer, C., Brice, A. K., & Marx, J. O. (n.d.). Intraperitoneal Administration of Ethanol as a Means of Euthanasia for Neonatal Mice (Mus musculus). Retrieved from http://www.ingentaconnect.com/contentone/aalas/jaalas/2017/00000056/00000003/art00009
Kosaraju, K., Lancaster, J. L., Meier, S. R., Crawford, S., Hurley, S., Aravamudhan, S., & Starobin, J. M. (2016). Non-invasive evaluation of cardiac repolarization in mice exposed to single-wall carbon nanotubes and ceria nanoparticles via intratracheal instillation. Environ. Sci.: Nano, 3(3), 611–618. http://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00225G







Request
Catalogue
Chat
Print